-

1
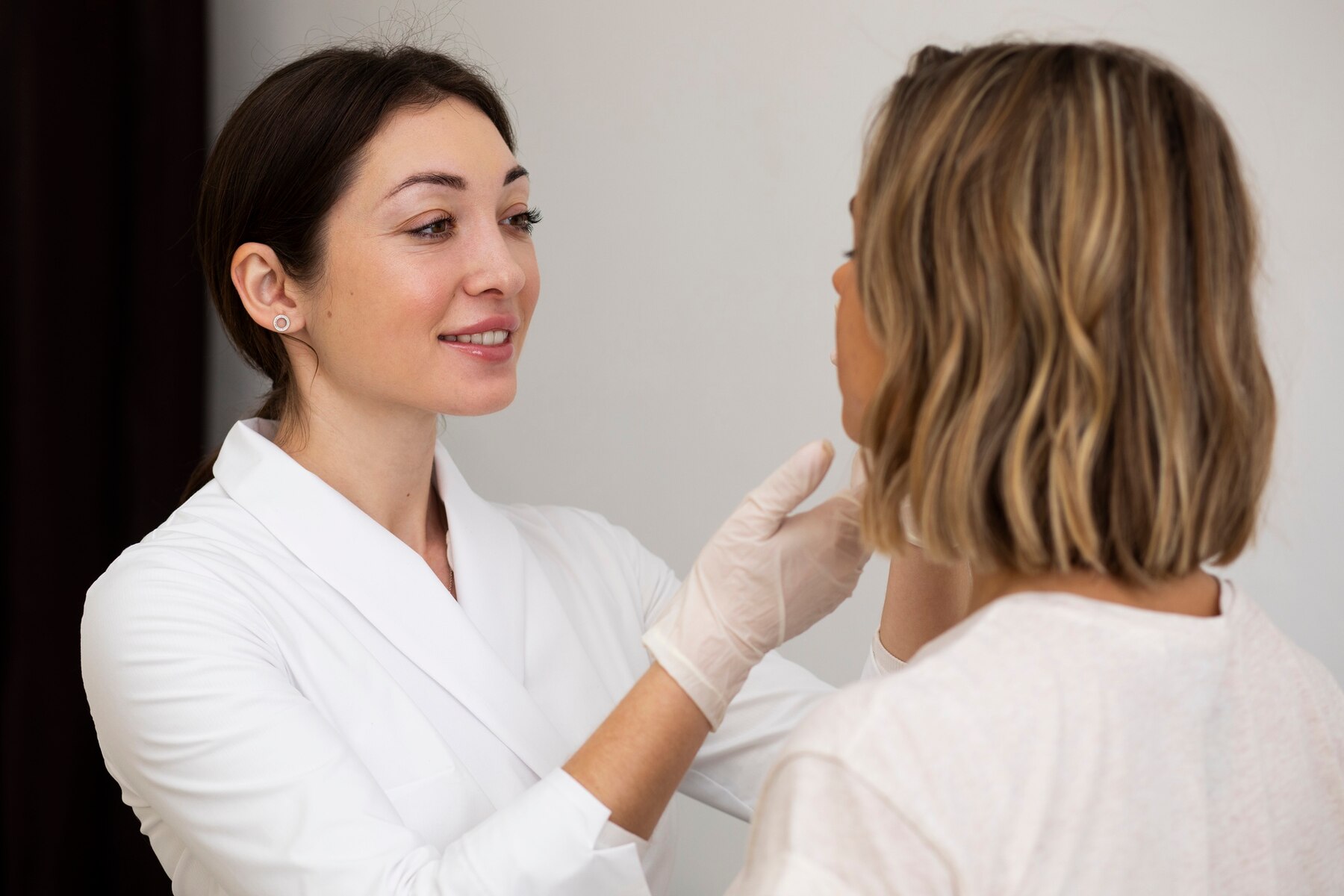
Consultation
Individuals undergo a consultation with a dermatologist or skincare specialist to assess the severity and extent of melasma, identify potential triggers, and determine the most suitable treatment options based on skin type, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
-

2
Identifying Triggers
Understanding potential triggers such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, and certain medications is crucial for managing melasma effectively. Individuals may be advised to avoid known triggers and adopt sun protection measures to prevent further pigmentation.
-
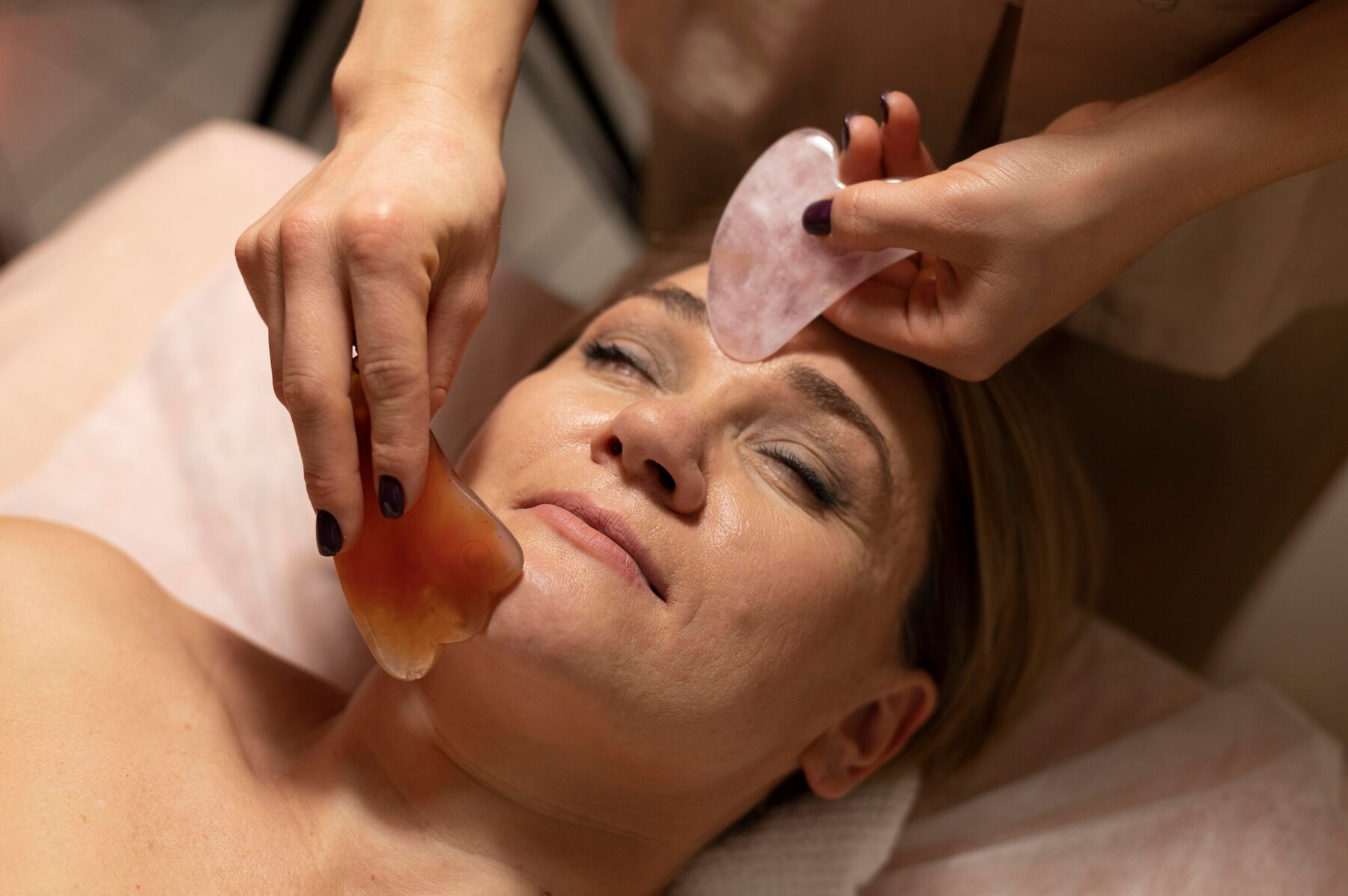
3
Topical Treatments
Topical medications containing ingredients such as hydroquinone, retinoids, corticosteroids, kojic acid, azelaic acid, or vitamin C may be prescribed to lighten pigmentation, inhibit melanin production, and promote skin renewal. These treatments are usually applied directly to the affected areas of the skin as part of a daily skincare routine.
-
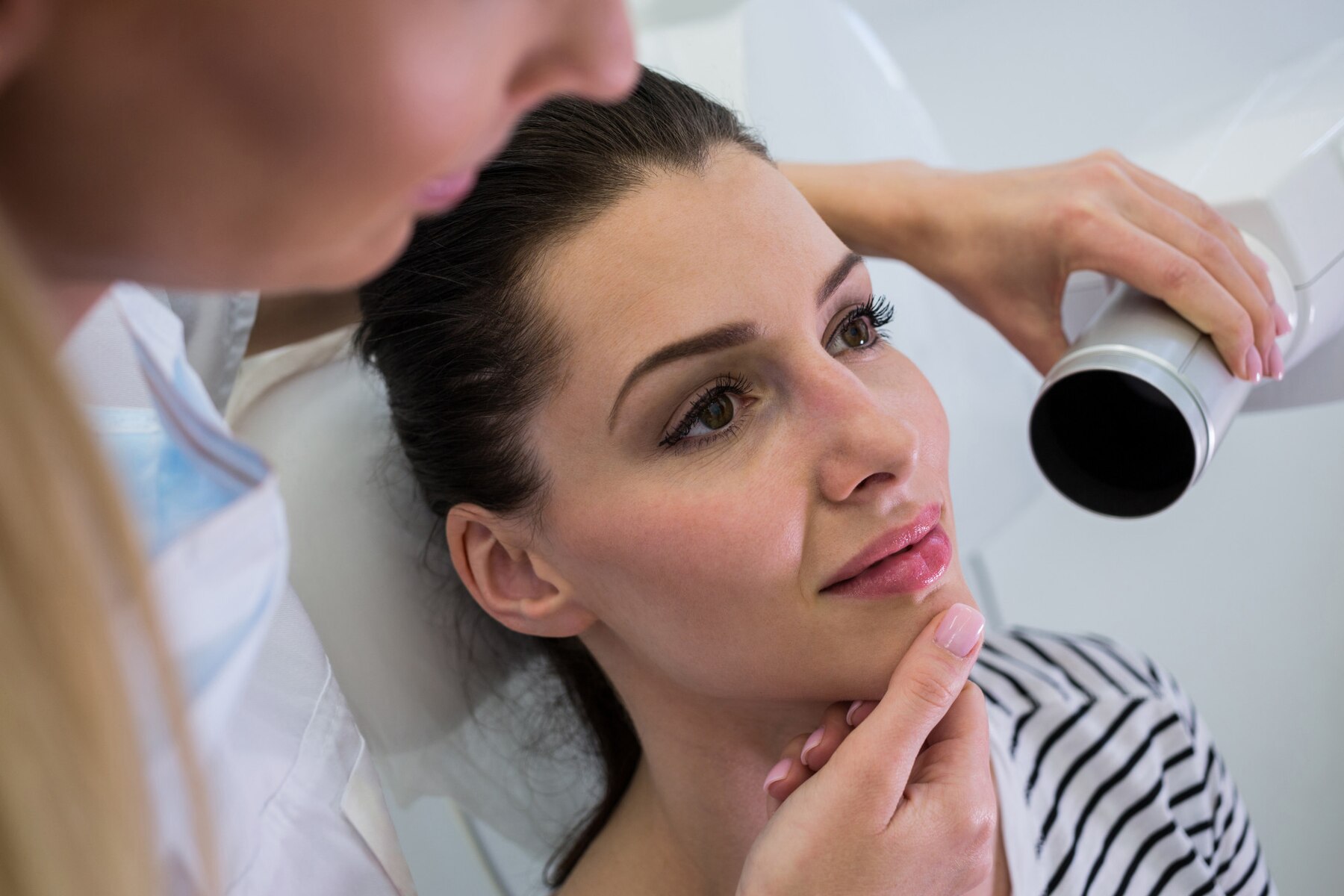
4
Professional Treatments:
In addition to topical treatments, professional procedures such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser therapy, or intense pulsed light (IPL) may be recommended to target stubborn pigmentation, improve skin texture, and enhance overall skin tone. These treatments are typically performed in a dermatologist's office and may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
-

5
Sun Protection
Sun protection is essential for preventing melasma from worsening and protecting the skin from further pigmentation. Individuals are advised to use broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours.